Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a critical nutrient that supports various bodily functions. From energy production to nerve health, it plays an indispensable role in overall well-being. For those looking to optimize their diet, knowing the best vitamin B12 foods to eat is essential. In this guide, we’ll explore its benefits, dietary sources, and tips for including it in your daily meals.
Why Is Vitamin B12 Important?
The Role of Vitamin B12 in Energy Production
Vitamin B12 aids in converting carbohydrates into glucose, a process vital for energy production. Without it, individuals often experience chronic fatigue, as their cells cannot efficiently generate energy.
Nervous System Health
Vitamin B12 protects the myelin sheath surrounding nerves, ensuring smooth communication between the brain and body. This protection helps prevent nerve damage and promotes cognitive health.
Heart and Pregnancy Benefits
For cardiovascular health, vitamin B12 regulates homocysteine levels in the blood, reducing the risk of heart disease. During pregnancy, it supports fetal brain and nervous system development, minimizing the chances of complications.
Animal-Based Vitamin B12 Foods to Eat
Meat and Poultry
Beef liver and chicken are two of the richest sources of vitamin B12. These foods provide a concentrated dose, helping individuals meet their daily requirements.
Seafood Options
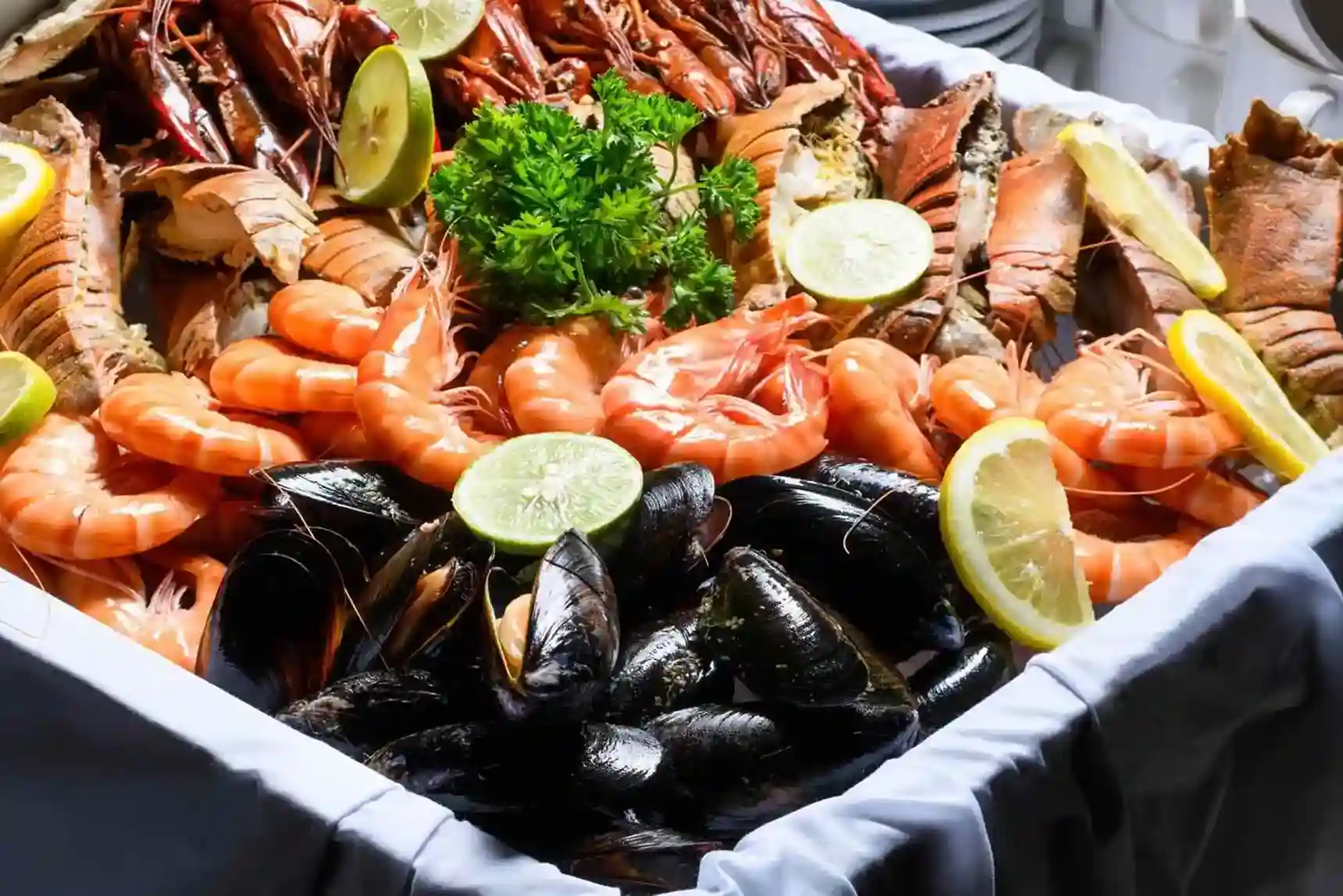

Clams, salmon, and tuna are excellent seafood choices. Not only are they high in vitamin B12, but they also contain omega-3 fatty acids, enhancing their health benefits.
Dairy and Eggs
Milk, cheese, and yogurt are suitable for vegetarians. Eggs are another versatile option that can be used in various meals, from breakfast dishes to baked goods.
Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B12

Fortified Foods for Vegans
Fortified cereals and plant-based milks like almond and soy are go-to options for vegans. They are specially enriched to provide adequate levels of vitamin B12.
Nutritional Yeast
This unique ingredient not only offers vitamin B12 but also enhances dishes with a cheesy flavor. It’s a popular choice among vegans and vegetarians.
Seaweed and Algae
While some seaweeds like nori contain trace amounts of vitamin B12, they are not reliable sources. Vegans should focus on fortified foods and supplements to meet their needs.
Health Benefits of Including Vitamin B12 Foods to Eat
Improved Energy Levels
By supporting glucose metabolism, vitamin B12 ensures sustained energy throughout the day. Many individuals notice a significant reduction in fatigue when they incorporate B12-rich foods.
Cognitive Function and Mental Health
Vitamin B12 supports neurotransmitter production, which regulates mood and brain function. It is especially beneficial for reducing the risk of depression and cognitive decline.
Heart Health
Regular intake of vitamin B12 lowers homocysteine levels, protecting against cardiovascular diseases. This is vital for individuals with a family history of heart-related conditions.
How to Include Vitamin B12 Foods in Your Diet
Breakfast Ideas
Start your day with fortified cereals paired with plant-based milk. Eggs can also be prepared in various ways, such as scrambled or in an omelet.
Lunch and Dinner Suggestions
Seafood like salmon or tuna works well for main dishes, while lean beef liver can add a rich flavor to meals. Vegans can use nutritional yeast to enhance soups or pasta.
Snacking Options
Cheese sticks or a glass of fortified plant-based milk are convenient snacks that provide vitamin B12. When dining out, opt for dishes featuring seafood or fortified alternatives.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Fatigue and Weakness
One of the earliest signs of deficiency is persistent tiredness, even after adequate rest. This occurs due to reduced oxygen transport caused by fewer red blood cells.
Neurological Issues
Tingling sensations in the hands and feet, known as peripheral neuropathy, are common symptoms. Severe deficiencies may lead to memory loss or difficulty concentrating.
Mood Swings and Depression
Low levels of vitamin B12 can disrupt brain chemistry, leading to irritability, mood swings, and even depression. Pregnant women may face complications if their levels are insufficient.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Adequate Vitamin B12 Levels
Fortified Foods as Daily Staples
Incorporating fortified foods into your diet ensures you meet your B12 needs without much effort. These options are especially helpful for vegetarians and vegans.
Balanced Meal Planning
Plan your meals around foods that are naturally rich in vitamin B12. Pair these with other nutrient-dense ingredients to create well-rounded dishes.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you suspect a deficiency, consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and advice. They may recommend supplements or dietary adjustments based on your needs.
FAQs About Vitamin B12 Foods to Eat
Which foods are the richest in vitamin B12?
Beef liver, clams, salmon, and fortified cereals are some of the richest sources.
Can vegans meet their vitamin B12 needs through diet alone?
Vegans typically rely on fortified foods and supplements, as plant-based sources do not naturally contain sufficient amounts of vitamin B12.
What happens if you don’t consume enough vitamin B12?
A deficiency can lead to fatigue, nerve damage, and cognitive issues. Severe cases may cause permanent neurological damage.
Incorporating vitamin B12 foods to eat into your diet is essential for maintaining energy, brain health, and overall well-being. Whether you rely on animal products, fortified foods, or supplements, there are numerous ways to ensure you meet your daily needs. Understanding its importance and making conscious dietary choices can significantly enhance your quality of life.